A Comprehensive Guide for DVD Resolution - Enhancement & More
Are you trying to get the most out of your DVD resolution so you can enjoy more entertainment at home? Explore our in-depth guide as we explain the nuances of DVD resolution, covering everything from improving visual fidelity to comprehending baseline resolutions. Learn about the variables that affect DVD resolution, compare it to other video formats, and get tips and advice on improving your viewing experience.

Part 1. DVD Resolution Introduction
DVD resolution is an essential component of your home entertainment. Learn about standard DVD resolutions and the significance of aspect ratios and pixel aspect ratios.
Standard DVD Resolution:
• NTSC or National Television System Committee: The standard resolution for NTSC DVDs is 720×480 pixels. NTSC is the video standard used in North America, Japan, and some other regions.
• PAL or Phase Alternating Line: The standard resolution for PAL DVDs is 720×576 pixels. PAL is the video standard used in Europe, Australia, parts of Asia, and other regions.
Aspect Ratio and Pixel Aspect Ratio:
• Aspect ratio: The proportionate relationship between the width and height of a video frame is known as the aspect ratio. The two most popular aspect ratios for DVDs are 4:3 for standard and 16:9 for widescreen. Older television sets usually have an aspect ratio of 4:3, whereas newer TVs and home entertainment systems employ a widescreen format of 16:9.
• Pixel Aspect Ratio: The definition of the individual pixel's shape in a display is determined by the pixel aspect ratio. Pixels with a pixel aspect ratio of 1.0 for standard DVD quality are typically square. Some pixel aspect ratios, however, may vary to support widescreen monitors without distorting the image, as with anamorphic widescreen DVDs.
Part 2. Comparison with Other Video Resolutions
This table provides a clear comparison of the different resolutions in terms of their dimensions, aspect ratios, common usage scenarios, and more.
| Resolution | Dimensions (pixels) | Aspect Ratio | Common Usage | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DVD (SD) | 720×480 (NTSC) | 4:3 | Standard definition video, older TVs, DVDs | - Interlaced video (fields) |
| 720×480 (NTSC) | 4:3 | - Often encoded in MPEG-2 format | ||
| HD (720p) | 1280×720 | 16:9 | Broadcast television, streaming services | - Progressive scan - Better picture quality than DVD |
| Full HD (1080p) | 1920×1080 | 16:9 | Blu-ray discs, streaming services | - Progressive scan - Offers higher resolution than HD (720p) |
| 4K (UHD) | 3840×2160 (UHD) | 16:9 | High-end TVs, streaming services, gaming | - Offers four times the resolution of Full HD (1080p) |
| 4096×2160 (True 4K) | 17:9 | - True 4K resolution is commonly used in professional cinema |
Part 3. Factors Influencing DVD Resolution
Here are the factors shaping DVD resolution: from technical constraints to market demands, these elements define the standards we rely on today.
• Technical Restrictions: In order to balance quality and capacity, DVD resolution was impacted by storage and data transfer limitations in the 1990s.
• Compatibility: To guarantee worldwide playing compatibility, DVD resolution must conform to NTSC and PAL standards.
• Data Storage: A limited DVD capacity necessitates balancing resolution to fit content inside the available area effectively.
• Playback Hardware: DVD resolution works with current televisions and playback devices without requiring expensive modifications for users.
• Cost considerations: DVD resolution struck a compromise between affordability and visual quality for both production and the manufacture of consumer products.
• Market Demands: DVD resolution was enough for the then-current display technology because there was little demand for high-quality material.
• Adoption of Standards: By standardizing DVD resolution, producers and regions could ensure broad compatibility, encouraging customer acceptance, new DVD releases, and adoption.
Part 4. Enhancing DVD Resolution
Tipard DVD Ripper emerges as the premier choice when considering ways to enhance DVD resolution. With its capacity to convert DVDs to more than 500 video formats while preserving quality and offering advanced editing features, it serves as the top solution for optimizing DVD visual fidelity. Below is a comprehensive step-by-step guide.
Step 1 To begin, download and install the Tipard DVD Ripper on your computer.
Step 2 Next, open the utility after it has finished installing, then select the Load DVD Disc option.
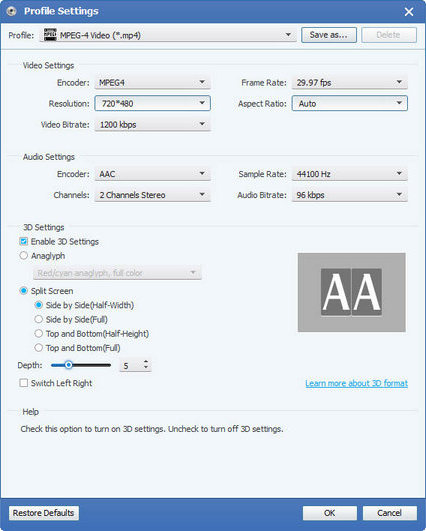
Step 3 Then, in the Profile Settings box, you may adjust the video and audio parameters, including the video encoder, frame rate, resolution, aspect ratio, bitrate, sampling rate, channels, and bitrate, to get the best DVD resolution.
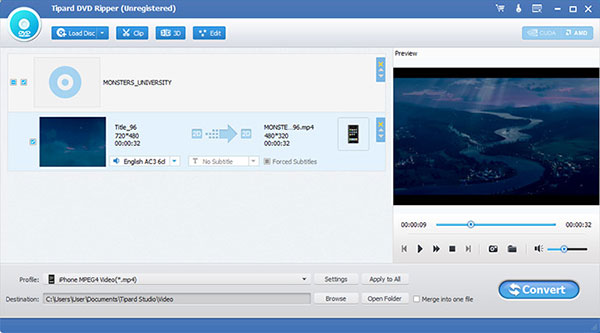
Step 4 Furthermore, you can edit the video's orientation, apply 3D settings, customize the video frame, enhance video effects, and adjust volume levels. The interface provides clear guidance for these adjustments.
Step 5 Finally, tap on the Convert button to start ripping the video. Wait for the process to finish, and you're done! You can rip the DVD to computer and watch it on different platforms.
Part 5. FAQs on DVD Resolution
Does the quality of video on current TVs depend on the DVD's resolution?
A modern TV's video quality can be affected by the resolution of a DVD, yes. When playing DVDs on high-definition televisions, as opposed to contemporary HD or 4K video, their lower resolution might cause a loss of clarity and detail. However, some quality limitations can be mitigated to improve the viewing experience because of technological breakthroughs in upscaling.
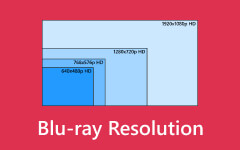
Which is better, Blu-ray quality or DVD resolution?
When it comes to standard definition video, DVD resolution usually falls between 720×480 and 720×576 pixels. On the other hand, Blu-ray discs offer superior clarity and detail because of their compatibility with Full HD resolutions of up to 1920×1080 pixels. Regarding image quality, Blu-ray surpasses DVDs because of its improved video encoding and better resolution.
Are NTSC and PAL standards for DVD resolution different from one other?
According to NTSC and PAL standards, DVD resolution does differ. 720×480 pixels is the standard resolution for NTSC DVDs and 720×576 pixels for PAL DVDs. These modifications account for how different regions across the world use the NTSC and PAL video standards, which have different frame rates and aspect ratios.
Could editing software improve the resolution on a DVD?
Editing software does not allow for significant resolution enhancements over the original DVD. The DVD format's inherent resolution constraints don't alter, even though specific software might provide marginal gains by boosting clarity or using upscaling techniques. Better video quality can be achieved more successfully by upgrading to higher-resolution formats like Blu-ray.
Does DVD resolution optimization require any particular settings?
Indeed, some settings maximize DVD resolution. Images can be made of higher quality by adjusting parameters like bitrate, aspect ratio, resolution, frame rate, and video encoder. Higher bitrates and preserving the original aspect ratio can also assist in reducing artifacts and preserving details, improving the resolution of the DVD when it is being played back.
Conclusion
Thanks to this article, you now know the dimensions of a DVD resolution, why it matters for home entertainment, and how to improve the quality of the images. You may maximize your viewing experience by knowing about standard resolutions and investigating elements that affect DVD resolution. Become the director of your entertainment and unleash the whole cinematic experience that DVD resolution offers.