Uncover How Many MBs are in a GB, Ways to Convert & Best Compressor to Use
Data storage and file sizes are often expressed in kilobytes or KB, megabytes or MB, gigabytes or GB, and terabytes or TB. Understanding the differences between these units is crucial for effectively managing digital information. Whether you're uploading files, downloading media, or simply organizing your computer, knowing the distinctions between these measurements can significantly impact your digital experience.
This article will explore the nuances of KB, MB, GB, and TB, explaining their significance and relationship. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of these units, empowering you to navigate the vast realm of digital data with confidence, like knowing how many MB are in a GB and so on.

- Part 1. Memory & Memory Units - What It Is?
- Part 2. Know More about the Types of Various Units of Memory
- Part 3. KB vs. MB vs GB vs. TB - A Comprehensive Comparison Chart
- Part 4. How to Convert Memory Units - KB to MB, MB to GB, GB to TB & More
- Bonus: Best Way to Compress File Size from GB to MB and Save More Storage Space
- Part 5. FAQs about the Differences of KB, MB, GB and TB
Part 1. Memory & Memory Units - What It Is?
Memory is the backbone of every operation, allowing computers and electronic devices to store, access, and manage data. Memory, in this context, refers to the electronic components within a device that store and retrieve information. These components are crucial for the seamless functioning of computers, smartphones, tablets, and other daily gadgets.
As we dive into it, we can see that memory can be expressed in four types, known as memory units. These are the kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes we mentioned earlier in the introduction, and they are used to quantify the amount of data a device can store internally. To understand more, let’s break down these memory units and see their significance.
1. Kilobyte or KB
Kilobyte is the smallest unit of memory commonly used in digital technology. One kilobyte is equivalent to 1024 bytes. It might sound small in today’s context, but with it, you can store plain text or basic program instructions.
2. Megabyte or MB
What does a megabyte mean? It is more significant than a kilobyte and equals 1024 kilobytes or 1,048,576 if it is in bytes. It can hold more data than the previous one, making it suitable for storing documents, images, and low-res or short video clips.
3. Gigabyte or GB
Gigabyte memory is commonly found in modern computers and external storage devices since a GB equals 1,024 megabytes if you convert MB to GB. It can accommodate larger files, software applications, and extensive multimedia content on your device.
4. Terabyte or TB
Terabyte is the next step for GB, essential for managing vast amounts of data, such as high-definition videos, complex software programs, and extensive databases. How many GB in a TB? For a terabyte, it equals 1,024 gigabytes or 1,099,511,627,776 bytes in total.
Part 2. Know More about the Types of Various Units of Memory
Understanding the types of memory units is essential for making informed decisions about data storage and management. To know the various memory units, you can read the information we have added below.
1. Random Access Memory or RAM
RAM is a volatile memory used by computers and other devices to store data that the processor needs to access quickly and temporarily. Unlike permanent storage, like hard drives or SSDs, Random Access Memory loses its data when the power is turned off or the device is restarted. RAM is measured in gigabytes or GB and directly impacts a device's speed and multitasking capabilities. More RAM allows for smoother performance when running multiple applications simultaneously.

2. Read-only Memory or ROM
ROM is a non-volatile memory that stores data permanently. Unlike RAM, ROM retains its data even when the power is turned off. It is commonly used in devices to store firmware or software essential for booting up the system. ROM chips contain instructions that the computer uses to initialize hardware components and perform the booting process.

3. Hard Disk Drives or HDD
HDDs are magnetic storage devices used in computers to store GB to TB data persistently. They consist of one or more magnetic disks on which data is written and read using magnetic heads. HDDs offer large storage capacities, often measured in terabytes or TB, commonly found in desktop computers and external storage devices.

4. Solid-state Drive or SSD
SSDs are newer storage devices using NAND-based flash memory to store data. Unlike the previous one, SSDs have no moving parts, making them faster, more durable, and energy-efficient. SSDs are widely used in laptops, smartphones, and modern desktop computers. They provide faster data access and significantly improve overall system responsiveness.

5. Flash Drives or USB Drives
Flash drives, also called USB drives or thumb drives, use NAND flash memory that can store bytes to GB of data, or sometimes it can go up to TB. They are compact, lightweight, and offer various storage capacities, usually ranging from a few gigabytes to several terabytes. Flash drives are commonly used for transferring files between computers and creating backups due to their convenience and portability.

Part 3. KB vs. MB vs. GB vs. TB - A Comprehensive Comparison Chart
| Kilobyte (KB) | Megabyte (MB) | Gigabyte (GB) | Terabyte (TB) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approximate Equivalent | A few paragraphs of text | A medium size novel | A movie or a large PDF documents | More HD movies and an extensive storage of PDF documents |
| Common Uses | 1. Small text files 2. Basic documents 3. Email messages 4. Simple spreadsheets |
1. High-resolution images 2. Short videos 3. Minute of MP3 audio 4. All in Kilobytes |
1. Movies 2. Extensive music collections 3. Games 4. Library of e-books 5. Several hours of HD videos 6. All in Megabytes |
1. HD movies 2. Ultra-high-resolution games 3. Large-scale data storage 4. Extensive databases |
| How Many in Bytes | 1,024 bytes | 1,048,576 bytes | 1,073,741,824 bytes | 1,099,511,627,776 bytes |
| Pros | 1. Low power consumption 2. Inexpensive 3. Suitable for simple task |
1. Balanced capacity for various files 2. Used in standard USB drives 3. Suitable for moderate multimedia task |
1. Balanced capacity for multimedia files. 2. Used in standard USB drives 3. Suitable for moderate multimedia tasks |
1. Adequate for extensive multimedia libraries 2. Suitable for large software installation 3. Common in consumer devices 4. Suitable for extensive data analysis and backups. 5. Common in enterprise settings. |
| How Many in Bytes | 1. Minimal storage capacity 2. Not ideal for multimedia or complex applications 3. Becomes quickly insufficient for modern needs |
1. Limited for HD videos or extensive photo libraries 2. It may fill up quickly with high-res media 3. More is needed for large applications. |
1. Limited for UHD videos or extensive photo libraries 2. It may fill up quickly with multiple Ultra high-resolution media 3. There may need to be more for storing large applications. |
1. It might be limited to ultra-HD videos or substantial gaming installations 2. It may fill up quickly with 4k videos and high-end games 3. Not ideal for massive data storage 4. Expensive for individual 5. Requires careful organization to prevent data clutter |
Part 4. How to Convert Memory Units - KB to MB, MB to GB, GB to TB & More
Converting memory units allows us to comprehend the scale of data and choose appropriate storage solutions or manage file sizes effectively. The relationship between kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), and terabytes (TB) is based on powers of 2, making conversions straightforward once you grasp the fundamentals.
1. Convert Memory Units of Kilobytes
To Megabytes & Vice Versa:
How many KB is in an MB? You can divide the kilobyte by 1,024 since 1MB equals 1,024. For example, if you have 5,120 KB, you must divide that by 1,024, resulting in 5,120/1.024 equals 5 MB.
In the same way, you can get the memory unit of MB to KB by times. For example, if you want to know what the KB of 7 MB then you will need to times that to 1,024 since in every MB, there is a total of 1,024. The answer will be 7,168 KB.
To Gigabytes & Vice Versa:
How many KB in a GB? In every GB, there is a total of 1,073,741,824 KB. For example, if you have a photo collection totaling 15,000,000 KB, you must divide that by 1,073,741,824 to get the total GB of storage space it occupies, which is approximately 14.65 GB.
How about you get the total KB on the GB storage you have? How can you compute it? As we have done on MB, you must times the GB to 1,073,741,821 KB. For example, you have 3.56 GB storage; what you need to do is to time that into the total amount of KB, and the result is 3,822,520,882.76 KB.
To Terabyte & Vice Versa:
For every Terabyte, there is 1,099,511,627,776 KB in total. So, if you want to convert the TB to KB, you can divide the TB to 1,099,511,627,776 KB, and you will get the answer. But if you have a 5 terabyte storage capacity times that to 1,099,511,627,776 KB, you can store a staggering 5,497,558,138,880 KB of data.
2. Convert Memory Units of Megabyte
To Gigabyte & Vice Versa:
How many megabytes is a gigabyte? There is 1,024 MB in every GB you have on your storage. If you have a total of 26,214.4 MB in your storage space and want to get the total GB, you will need to divide that number by 1,024 since in every 1 GB, there is a total of this number, and the answer will be 25.6 GB.
If you want to convert GB to MB, what should you do? That is where you will need to use multiplication. For example, if you have a total of 56.963 GB and want to get the total MB, then you will need to multiply that by 1,024, and the result will be 58,330.112 MB.
To Terabyte & Vice Versa:
The conversion for every 1 TB to MB is 1,073,741,824 MB. So, if you have a 3,221,225,472 MB, you must divide that by 1,073,741,824, and the answer will be 3 TB. To do the other way, if you have a 58.6 TB database, times that by the total MB, you will get 62,921,270,886.4 MB of storage space on your database.
3. Convert Memory Units of GigaByte
To Terabyte & Vice Versa:
Likewise, if you have a TB, you will get 1,024 GB. For example, if you want to convert GB to TB, then you will need to perform division. The total storage space that is needed to get the game you want to play is 26,996 GB, and if you want to know what is the total TB, try to divide that by 1,024, and you will get approximately 26.36 TB.
What if you want to get the total GB on TB? What should you do? You will need to multiply the total amount of TB to 1,024 GB. For example, you have a digital database that has a 736.45 TB. To get the total GB, you must multiply that by 1,024, and the result is 753,664 GB.
Bonus: Best Way to Compress File Size from GB to MB and Save More Storage Space
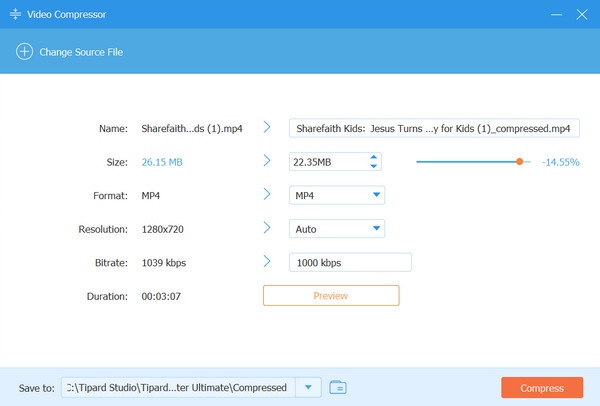
Media files saved on your computer, like videos and audio, can occupy some space, which may result in whole storage. With the help of Tipard Video Converter Ultimate, we can solve this problem immediately. Using the video/audio compressor feature to decrease the file size is the best choice since it is fast, reliable, and safe. Here, you can compress GB to MB, yet the quality is still intact on the file. You can try this app out by clicking the download button we have added for free.
Extended Reading:
Top 9 Most Outstanding File Size Reducer to Use of 2025
DVD Capacity: Discover the Size of Your DVD Collections
Part 5. FAQs about the Differences of KB, MB, GB and TB
Does converting videos make the file size smaller or bigger?
Converting videos can make the file size smaller or bigger, depending on the chosen format and compression setting that has been set to it.
Which is bigger, MB or GB?
Gigabyte is bigger than MB because 1 GB is equal to 1,024 MB.
Who named KB, MB, GB, and TB?
KB, MB, GB, and TB are derived from the metric system prefixes, where kilo means thousand, mega means a million, giga means a billion, and tera means a trillion. These terms have been widely adopted in the field of computing to represent different levels of data size.
What is the most prominent memory unit in the world?
Regarding data storage capacity, the most significant memory units in the world are measured in yottabytes or YB. One yottabyte is equal to 1,208,925,819,614,629,174,706,176 bytes.
Can I retrieve lost files on Android internal memory?
Yes, you can recover lost files on Android internal memory with the help of an application like Tipard Android Data Recovery.
Conclusion
Finally, we already wielded knowledge about memory, memory units, ways to convert KB to GB, and many more. We hope that the information we deliver helps you to notice the differences between KB, MB, GB, and TB. Suppose your media file size is too big to contain on your computer. In that case, you can use the Tipard Video Converter Ultimate to compress it without compromising the overall video quality.







