Detailed Tutorial About DVD - Specifications, Structure, and More

As technology progressing, more and more people turn to PCs and other digital devices to watch videos. So, some analysts have expected that DVD and DVD players would dead from customer market. However, such argument does not become reality. In the contrary, DVD has evolved to more advanced formats, such as Blu-ray DVD and re-emerged in customer market. On the other hand, DVD is still an important medium to enjoy high quality movies on larger screen, like HDTV. Moreover, as a powerful storage, DVDs are useful in data sensitive industries. But what is DVD? How much data a DVD could store? And how high the DVD resolution is? In this article, you can find all the knowledge you should know about DVD.
Part 1: What is DVD
DVD history
DVD stands for Digital Versatile Disc or Digital Video Disc and was developed jointly by Philips, Sony, Toshiba and Panasonic in early 1990s. It's a kind of digital optical disc storage format with a higher resolution pictures and sound than VHS. Also, DVD offers a larger storage capacity over compact discs (CD) and can be used to store video, audio, and other data like documents, pictures, programs, etc. DVD has several disc types including DVD-R/RW, DVD+R/RW, DVD-RAM, and DVD ROM. Commercial DVDs employ encryption methods in order to protect contents from copying without authorizing. So it'll be pretty hard to rip DVD to computer.
DVD types
DVD has various disc types, including DVD-R, DVD+R, DVD-RW, DVD+RW, DVD-RAM and DVD-ROM. The letter "R" refers to Recordable and can only be recorded once via DVD recorder. "RW" means Rewritable while "RAM" stands for Random Access Memory and these two kinds of discs can be recorded and erased many times. DVD-ROM (Read Only Memory) refers to the pre-recorded DVDs mass-produced by molding machines and can only be used for playing in DVD drive/players by customers.
Another common DVD format is HD DVD. Movie enthusiasts are familiar with HD DVD very much. HD DVD is short for high definition disc used to store data and playback of high-definition video. HD DVD was the successor to the standard DVD format.
DVD capacity and resolution
The most important thing to customer is the resolution of a DVD. Generally speaking, the DVD resolution is decided by its storage capacity. The more data a DVD stores, the higher the resolution of the movie on the DVD.
| Format | DVD 5 | DVD 9 | HD DVD | Blu-ray DVD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTSC Resolution | 720×480 | 720×480 | 1920×1080 | 1920×1080 |
| PAL Resolution | 720×576 | 720×576 | 1920×1080 | 1920×1080 |
| Maximum Storage Capacity(per layer) | 4.7 GB | 7.95 GB | 15 GB | 25 GB |
| Recording Time | 100-135 minutes | 20-240 minutes | ||
| Quality | Standard | Good | Better | Excellent |
Part 2: DVD Specifications
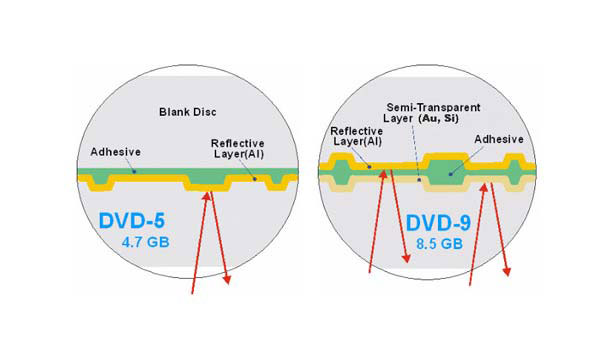
DVD-5 vs. DVD-9
Among DVD format types available nowadays, DVD-5 and DVD-9 are the most widely used DVD types. DVD 5 adopts single-sided single-layer 12cm standard DVD disc with a capacity of 4.37 GiB / 4.7GB. DVD-5 is the most widely used DVD media. DVD 9 uses single-sided dual-layer DVD disc with a size of 7.95 GiB / 8.5GB.
DVD-R vs. DVD+R
DVD-R and DVD+R use different writing specifications. These two DVD formats are nearly identical and are both supported by most DVD-ROM drives and DVD Burners. The only difference between the two disc types is the way they determine the location of the laser beam on the disc. The relationship between DVD-RW and DVD+RW is the same.
What is DVD DL?
Ordinary DVD discs uses Single-Layer recording technology while some adopts Dual-Layer recording with a larger capacity. You can distinguish Single-Layer and Dual-Layer recording DVD discs with the mark "SL" and "DL".
Notes: Some 8cm authoring DVD discs are used as camcorder media for storage of AVCHD videos. Also DVD discs can store other data except video or audio like text documents, pictures, etc.
Blu-ray vs. DVD
Blu-ray is the latest successor of standard DVD. As its name said, Blu-ray cover a layer of blue violet laser to read and write data; while standard DVD use red laser. The biggest difference between Blu-ray and standard DVD is storage capacity. A storage capacity of a dual layer Blu-ray is more than ten times a single layer standard DVD.

Part 3: Structure of DVD
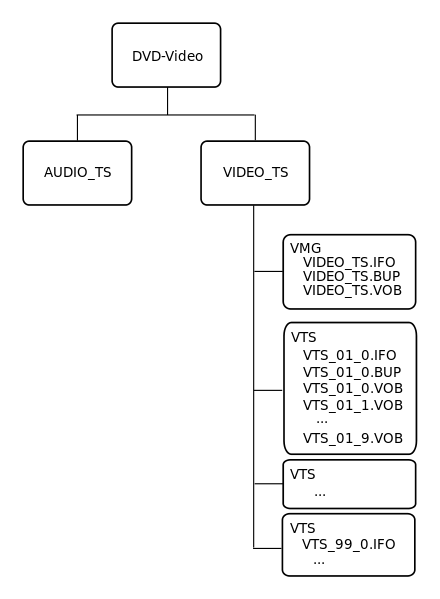
When accessing an internal or external DVD drive in a computer, you'll find 2 directories: AUDIO_TS and VIDEO_TS.
AUDIO_TS is used for storing DVD audio. The fact that this folder is always empty in a DVD Video disc doesn't mean there's no audio in the video. The directory only contains files on a DVD Audio disc.
VIDEO_TS is used for storing all data in the movie. Always there are two or more .IFO and .BUP files, and at least one VOB file in the folder. The BUP files are backup files of IFO files, which contain information like chapters, subtitles and audio tracks. And VOB files includes the video, audio, subtitle and menus of the DVD movie. The following is an example of DVD video structure:
Part 4: Restrictions of DVD
DVD Encryption
Commercially produced DVDs employ a Digital Rights Management (DRM) mechanism and adopt several encryption methods to protect its content from copying without permission.
The Content Scramble System
The Content Scramble System (CSS) is an encryption of DVD Video. It prevents unauthorized copy of DVD MPEG stream videos. It makes sure only certified DVD Players can play CSS encrypted DVDs and contributes a lot to the protection of intellectual property right.
Content Protection for Prerecorded Media
Content Protection for Prerecorded Media (CPPM) is the encryption mechanism DVD Audio discs adopt.
DVD Region Codes
DVD releases are separated into several areas. And Global region codes identify DVDs can only be played in DVD Players sold in the specific area.
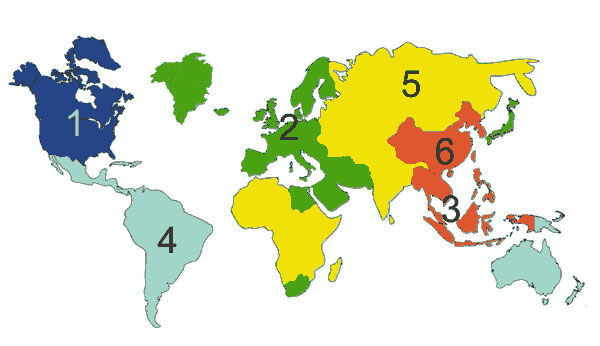
DVD Region Specifications
◆ Region 1: U.S., U.S. Territories, Canada, and Bermuda
◆ Region 2: Japan, Europe, South Africa, and the Middle East, including Egypt
◆ Region 3: East and Southeast Asia, including Hong Kong and Macau
◆ Region 4: Australia, New Zealand, Pacific Islands, Central and South America, and the Caribbean
◆ Region 5: Eastern Europe, Baltic States, Russia, Central and South Asia, Indian subcontinent, Africa, North Korea, and Mongolia
◆ Region 6: China
How to rip DVD with Restrictions
The restrictions make DVD discs rip a challenge, no matter which type of protection. But for DVD users, it is a necessary skill to rip DVDs since that is the best way to backup and protect the original DVD discs. From this point of view, we recommend Tipard DVD Ripper. This powerful tool could help you to rip DVDs and remove the restrictions.
Open DVD Ripper and insert the DVD you want to rip into your computer.
Click on the Load disc button to import video on DVD. DVD Ripper is able to detect the readable video files automatically.
Hit the Settings button on the bottom to open profile settings window. Unfold the drop-down list of Profile and choose an appropriate format. And reset other parameters according to your requirements.
After settings, click on the OK button to close the settings window. Once your hit the Convert button on the interface, DVD Ripper will start ripping the DVD. DVD Ripper allows you to rip a DVD to DVD, media folder or ISO file.
Conclusion
In this article, we introduced basic knowledge related to DVD. Now, you might understand what is DVD? How much data a DVD could store? And how high the DVD resolution is? Every coin has two sides, so does DVD. To protect copy right, organizations and institutions released multiple ways to prevent people copy DVDs without authorization. But that brings some troubles, when customers want to rip a DVD and protect the original one. So, we recommended you to use Tipard DVD Ripper to help you rip the region code or encryption protected DVD.







